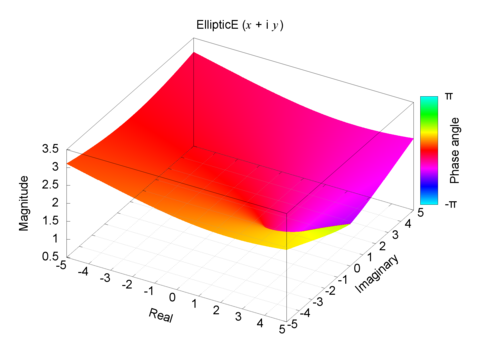
Complete Elliptic Integral of the Second Kind
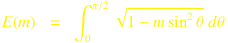
Dec. 27 2022
Takayuki HOSODA

The calculation is performed using the relationship between Complete Elliptic Integrals of the Second Kind and the Arithmetic Geometric Mean.
cEllipticE-1.0.tar.gz — The complete elliptic integral of the second kind. Rev.1.0 (Jan. 17, 2023) (c) 2022 Takayuki HOSODA
cEllipticE.c NAME _cEllipticE -- returns the complete elliptic integral of the second kind. LIBRARY Math library (libm, -lm)\n\ SYNOPSIS #include <math.h> #include <complex.h> #include <float.h> double complex _cEllipticE(double complex k); RETURN VALUE _cEllipticE(k) returns the complete elliptic integral of the second kind K(k).
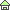
Formulas used/* cEllipticE - The complete elliptic integral of the second kind * Rev. 1.01 (Jan. 28, 2026) (c) 2022-2026, Takayuki HOSODA * SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause */ #include <math.h> #include <complex.h> #include <float.h> double complex _cEllipticE(double complex m); /** The complete elliptic integral of the second kind _cEllipticE(m) returns the complete elliptic integral of the second kind E(m) The argument m is the parameter m = k^2, where k is the elliptic modulus. K(m) &=& \int_0^{\pi / 2} \sqrt{1 - m \sin^2 \theta}\ d \theta */ double complex _cEllipticE(double complex m) { double complex a, b, s, c, p; double q, r; int i = 0; /* iteration counter */ int ITER = 60; a = 1.0; if (m == a) return a; b = csqrt(a - m); s = 1.0 - (a + b) * (a - b) * 0.5; /* sum, n = 0 */ c = 1.0; /* coefficient of powers of 2 */ r = DBL_MAX; do { q = r; p = s; m = csqrt(a * b); a = (a + b) * 0.5; b = ((cabs(a + m) == cabs(a - m)) && (cimag(m / a) > 0)) || (cabs(a + m) < cabs(a - m)) ? -m : m; s -= c * (a - b) * (a + b); c = c + c; if (++i > ITER) break; r = cabs(s - p); /* correction radius */ } while (r != 0 && q > r); /* convergence check */ /* Urabe's method is used to determine convergence, and assuming that the * arithmetic-geometric mean part converges faster than the series part, * convergence is determined only by the convergence of the series part. */ return M_PI * s / (a + b); } #ifdef DEBUG #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> char * help = "Name\n\ cEllipticE -- returns the complete elliptic integral of the second kind.\n\ Rev. 1.0 (Jan. 17, 2023) (c) 2022, Takayuki HOSODA (aka Lyuka)\n\ Usage\n\ cEllipticE m.re\n\ cEllipticE m.re m.im\n\ cEllipticE range_re range_im samples\n"; int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { double complex m; double complex c; double x, y; int n = 801; int r, j; if (argc == 2) { m = (atof(argv[1])); c = _cEllipticE(m); if (cimag(c) == 0) { printf("_cEllipticE(%.16g) ~= %.16g\n", creal(m), creal(c)); } else { printf("_cEllipticE(%.16g) ~= %.16g%+.16gi\n", creal(m), creal(c), cimag(c)); } }else if (argc == 3) { m = (atof(argv[1]) + I * atof(argv[2])); c = _cEllipticE(m); printf("_cEllipticE(%g %+gi) ~= %.16g %+.16gi\n", creal(m), cimag(m), creal(c), cimag(c)); } else if (argc == 4) { x = atof(argv[1]); y = atof(argv[2]); n = atof(argv[3]); if (n < 10) n = 10; printf("#Computed by \"_cEllipcK Rev.1.0 (Jan. 17, 2023) (c) 2022, Takayuki HOSODA (aka Lyuka)\n"); for (r = 0 ; r <= n; r++) { for (j = 0 ; j <= n; j++) { m = (-x * r + (n - r) * x) / n + I * ((-y * j + (n -j) * y) / n); c = _cEllipticE(m); printf("%.16g\t%.16g\t%.16g\t%.16g\n",creal(m), cimag(m), cabs(c), carg(c)); } printf("\n"); } } else { printf("%s\n", help); } return(0); } #endif
_cEllipticE(0) ~= 1.570796326794897 _cEllipticE(0.25) ~= 1.467462209339425 _cEllipticE(0.5) ~= 1.350643881047667 _cEllipticE(0.99) ~= 1.015993545025225 _cEllipticE(1) ~= 1 _cEllipticE(-1) ~= 1.910098894513857 _cEllipticE(2) ~= 0.5990701173677973+0.5990701173677941i _cEllipticE(0.25 +0.25i) ~= 1.473879994036591 -0.1082796079933554i _cEllipticE(1 +1i) ~= 1.283840957898245 -0.5317843366915171i _cEllipticE(-1 -1i) ~= 1.938813920750762 +0.2934621483557033i
E(0) ~= 1.570796326794896619 E(0.25) ~= 1.467462209339427155 E(0.5) ~= 1.350643881047675503 E(0.99) ~= 1.015993545025223936 E(1) ~= 1 E(-1) ~= 1.910098894513856009 E(2) ~= 0.599070117367796104 + 0.599070117367796104i E(0.25 +0.25i) ~= 1.473879994036592246 - 0.108279607993355404i E(1 + i) ~= 1.283840957898244583 - 0.531784336691518627i E(-1 + i) ~= 1.938813920750761868 - 0.293462148355703310i
![[Mail]](/~lyuka/images/mail.gif)

 © 2000 Takayuki HOSODA.
© 2000 Takayuki HOSODA.